The digital revolution in healthcare
Digital health interventions such as wellness, self-care and activity apps have been shown to promote healthy behaviours such as smoking cessation, reduced alcohol intake, support with exercise, and eating a healthy diet⁶. Furthermore, recent evidence shows they can improve outcomes for patients with long-term conditions⁶'⁷'⁸'⁹, and importantly, they can improve accessibility to health-related information. Pre-pandemic the uptake of digital health technologies was slow²'¹⁰, however with the emergence of COVID-19, they became an immediate necessity and digital health adoption was greatly accelerated within healthcare service delivery¹¹'¹². NHS Digital reported a 111% usage increase in NHS app registrations¹³.
Despite digital health interventions offering numerous benefits, a great challenge is promoting uptake and engagement¹⁴'¹⁵'¹⁶. Making an App available to clinical teams and patients is unlikely to be enough to drive adoption and engagement. Instead, when deploying a solution, it’s imperative that the local needs of healthcare teams and their patients are considered carefully and a personal approach is taken. To ensure healthcare teams receive the necessary support to implement digital self-management apps with a personal touch, my mhealth created the Digital Health Adviser (DHA).
The Digital Health Adviser
my mhealth recognised there was a need to create person-centred digital app delivery and support which led to the development of the DHA. By bringing together the tec hnology and the needs of the service the perceived ‘heavy lift’ challenge of a digital transformation project has been reduced.This role works in partnership with my mhealth and the healthcare provider using an honorary contract. The healthcare team provides them with a list of patients to contact and offer the app(s). Those patients who would like to use the app(s) are offered guidance on how to use and are signposted to content related to goals set by the clinical teams. Similarly, the DHA’s support clinicians to engage with the technology, providing them with the skills to support, enhance and scale their service.
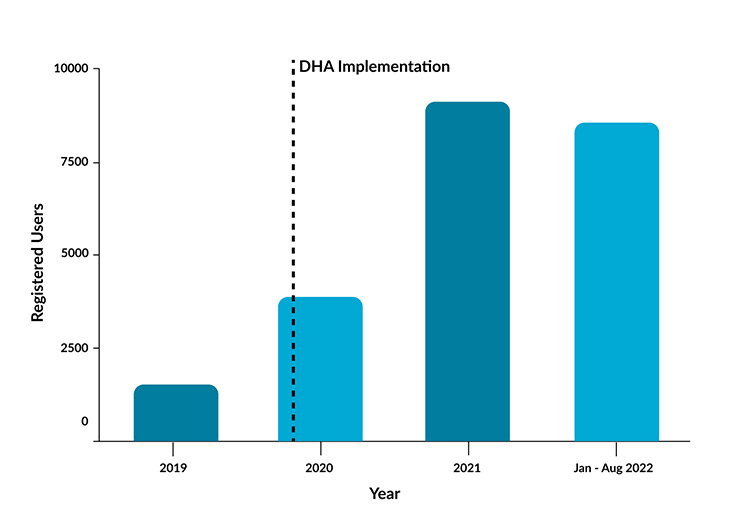
Since the creation of this new role, the benefits became evident very quickly. As a result, we now have a team of DHA’s working with NHS healthcare services across the country. They bridge the gap between the digital health platform, the clinician and the patient to support app uptake and engagement. Importantly, they promote digital inclusion and encourage the creation of local community digital champions. Figure 1 shows the increase in app usage for just five NHS sites since the DHA role was implemented.
- Case StudiesIn Mid and South Essex (MSE) DHA support was provided to compliment a drive from the clinical services to engage patients in myDiabetes. This saw an increase in app registrations from 1654 to 6356 users within 2 years, demonstrating a 284% increase. Furthermore, within 1 year in-app education video activity increased from 10,316 to 21,272
- Knowsley saw an increase in app registration from 277 to 3788 following DHA implementation over 2 years (1267% increase)
- Using the DHA, Cambridge and Peterborough CCG provided continuous access to education and self-management support using myAsthma, promoting equal access to the service for the local population. Nine practices with the highest healthcare utilisation were provided with 900 myAsthma licenses. All of these were supplied to patients within 6 months, of which 720 (80%) of patients activated the app.
- Kent and Medway CCG have registered over 6000 patients to the myDiabetes app in support of Structured Diabetes Education, driving a 200% increase in enrolment to the programme in 18 months.
Providing the ‘human’ connection in digital health Studies have shown that providing ‘human’ support in digital health interventions improves patient engagement¹⁷. The DHA is the person-link between digital health apps, clinicians and patient users, providing a structured route for the implementation of digital therapeutics into the NHS at population scale, reaching high levels of user engagement. The interaction of the DHA with clinical teams is vital to increasing confidence in using technology for both clinicians and patients, working towards reducing digital exclusion. The DHA’s are in constant contact with clinical teams to support their service and patients to encourage usage to promote self-management. They are also able to obtain important feedback of how the app(s) are functioning in the real-world.
Some comments received from clinical teams are:
“The DHA oversees the smooth running of patients who sign up for the app. They help patients with their many queries, and help the admin team to contact patients to take up the App. I could not do this part of my job without their input. Aside from the obvious impact they have on our patient’s education and management of their health, they are also enthusiastic and have a ‘can do’ attitude which really makes a difference when trying to encourage patients to use the app modules. They make my job much easier. I am so grateful for their help and feel totally supported at all times.”
(Healthcare Administrator)
“Working with my mhealth and the DHA’s has been invaluable to our practice. Their help and support has enabled them to give patients an informed choice on how to manage their chronic disease. Not only has this taken pressure off general practice it has given people the tools they need to improve and manage their own health.”
(Nurse Specialist)
Feedback from patients receiving DHA support include:
“Without your help I would have been 'out' of the my mhealth app for ever! Thank you so much for your patience and help with getting me started.”
“I have completed the exercises in Lifestyle tile is there another exercise tile or do I repeat what I have already completed? Your help would be appreciated.”
“Thank you for helping me - it's been a life changer for me and you can quote me on that.”
“For me personally to have someone as supportive as the DHA is as and when you need is invaluable. Diabetes is scary I'm still pretty new at finding out but the way your life works around it but with the proactiveness and correspondence and the regular updates from the DHA I don't know where I would be without it.”
As more healthcare services look to benefit from this support, the DHA team is expanding to meet the growing demand. Clinical partners are demonstrating a true step-change in the delivery of digital health to support healthcare delivery at population scale. Importantly, patients are provided with support both digitally and personally to self-manage their long-term condition without losing the human connection with their clinical teams.
- References
Gardner T. Pressures on the NHS are far from ‘sustainable’ [Internet]. The Health Foundation. 2021 [cited 2022 Aug 24]. Available from: https://www.health.org.uk/news-and-comment/news/pressures-on-the-nhs-are-far-from-sustainable - Peek N, Sujan M, Scott P. Digital health and care in pandemic times : impact of COVID-19. BMJ Heal Care Informatics [Internet]. 2020;27:1–3. Available from: https://informatics.bmj.com/content/27/1/e100166
- Royal College of General Practitioners. Chronic shortage of GPs is the reason patients are facing long waiting times for appointments [Internet]. RCGP. 2021 [cited 2022 Aug 24]. Available from: https://www.rcgp.org.uk/news/2021/september/chronic-shortage-of-gps-is-the-reason-patients-are-facing-long-waiting-times-for-appointments
- United Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS Trust. Waiting for your outpatient appointment during the COVID-19 Pandemic [Internet]. NHS Trust. 2021 [cited 2022 Aug 24]. Available from: https://www.ulh.nhs.uk/patients/outpatients/waiting-for-your-outpatient-appointment-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/
- Bene BA, O’Connor S, Mastellos N, Majeed A, Fadahunsi KP, O’Donoghue J. Impact of mobile health applications on self-management in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Protocol of a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019;9(6).
- Murray E, Hekler EB, Professor A, Andersson G, Collins LM, Doherty A, et al. Evaluating digital health interventions: key questions and approaches HHS Public Access Background & Aims. Am J Prev Med [Internet]. 2016;51(5):843–51. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5324832/pdf/nihms850074.pdf
- Murray E, Ross J, Pal K, Li J, Dack C, Stevenson F, et al. A web-based self-management programme for people with type 2 diabetes: the HeLP-Diabetes research programme including RCT. Program Grants Appl Res. 2018;6(5):1–242.
- Crooks MG, Elkes J, Storrar W, Roy K, North M, Blythin A, et al. Evidence generation for the clinical impact of myCOPD in patients with mild, moderate and newly diagnosed COPD: a randomised controlled trial. ERJ Open Res [Internet]. 2020;6(4):00460–2020. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/23120541.00460-2020
- Nabutovsky I, Nachshon A, Klempfner R, Shapiro Y and TR. Digital Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs: The Future of Patient-Centred Medicine. Telemed e-Health [Internet]. 2020;26(1):34–41. Available from: https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/tmj.2018.0302#:~:text=These programs imply a high level of patient,no significant differences in mortality or hospitalizations
- Pillay R. Digital Health Trends [Internet]. 2021. Available from: https://www.iqvia.com/-/media/iqvia/pdfs/institute-reports/digital-health-trends-2021/iqvia-institute-digital-health-trends-2021.pdf?&_=1630938621119
- National Diabetes Audit. Improving attendance and data recording for structured education. 2018; Available from: https://www.diabetes.org.uk/resources-s3/2018-12/SE Guidance_ v3.pdf
- DESMOND. MyDESMOND eLearning Platform [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2020 Sep 25]. Available from: https://www.desmond-project.org.uk/portfolio/mydesmond-elearning-platform/
- Poinasamy K. Useful Digital Health Apps and Platforms [Internet]. BLF and Asthma UK. 2022 [cited 2022 Feb 7]. Available from: https://www.asthma.org.uk/support-us/campaigns/campaigns-blog/useful-digital-health-apps-and-platforms/
- McGowan PT. Self-Management Education and Support in Chronic Disease Management. Prim Care Clin Off Pract [Internet]. 2012;39(2):307–25. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S009545431200019X?via%3Dihub
- Murray E, Sweeting M, Dack C, Pal K, Modrow K, Hudda M, et al. Web-based self-management support for people with type 2 diabetes (HeLPDiabetes): Randomised controlled trial in English primary care. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):1–11.
- Torous J, Myrick KJ, Rauseo-Ricupero N, Firth J. Digital mental health and COVID-19: Using technology today to accelerate the curve on access and quality tomorrow. JMIR Ment Heal. 2020;7(3):1–6.
- Ritterband LM, Thorndike FP, Cox DJ, Kovatchev BP, Gonder-Frederick LA. A behavior change model for internet interventions. Ann Behav Med. 2009;38(1):18–27.
About my mhealthmy mhealth’s digital therapeutics have been prescribed to over 80,000 patients with chronic conditions, resulting in reduced morbidity and hospital admissions. It serves patients across a range of long term conditions, including COPD, asthma, diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Our flagship product, myCOPD, was the exclusive digital therapeutic deployed by the UK’s NHS to deliver pulmonary rehabilitation during the pandemic, when in person care was practically inaccessible. Real world and clinical trial evidence demonstrates the efficacy of digital interventions on the my mhealth platform.
For more information on my mhealth, visit www.mymhealth.com.